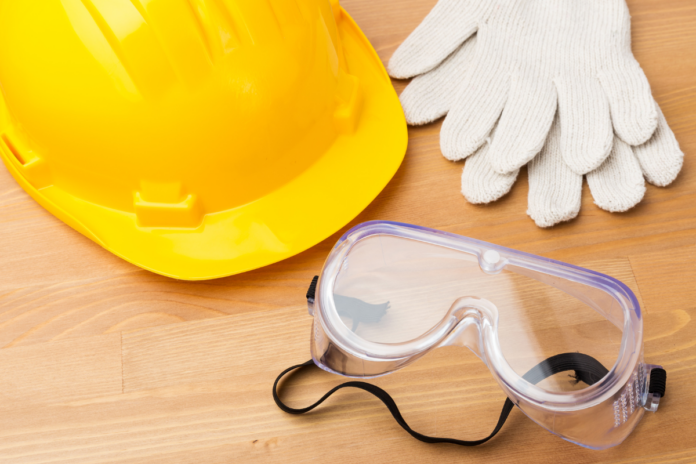
When it comes to looking for tank equipment online, safety should always be the top priority. Proper adherence to safety standards not only protects workers but also ensures compliance with regulatory requirements. Tank cleaning operations require strict safety procedures to prevent accidents and injuries, particularly when dealing with confined spaces.
Tank entry and cleaning present specific hazards that demand special attention. Employers must develop comprehensive procedures for recommissioning tanks after cleaning operations, including safety checks and proper use of personal protective equipment. These procedures should align with OSHA’s permit-required confined spaces standard, which outlines essential safety measures for entering potentially hazardous environments.
Implementing a robust safety plan for tank equipment usage involves multiple aspects, from fall protection to atmospheric testing. Regular training, proper equipment maintenance, and clear communication protocols are crucial components of an effective safety program. By prioritizing these elements, companies can create a safer work environment and minimize risks associated with tank operations.
Key Takeaways
- Safety procedures for tank equipment must comply with OSHA standards and industry best practices
- Confined space entry requires specialized safety protocols and permit systems
- Comprehensive training and proper equipment are essential for safe tank operations
Establishing Safety Procedures and Compliance Standards
Safety procedures and compliance standards are crucial for using tank equipment safely. These measures protect workers, prevent accidents, and ensure regulatory adherence.
Personal Protective Equipment and Safety Gear
Proper PPE is essential when working with tank equipment. Workers must wear hard hats, safety glasses, and steel-toed boots. Chemical-resistant gloves and coveralls protect against hazardous substances.
Respiratory protection may be necessary depending on tank contents. Face shields offer additional protection during certain tasks. Fall protection equipment is required for work at heights.
Regular inspection and maintenance of PPE is vital. Replace damaged or worn items immediately. Employers must provide appropriate PPE and ensure its proper use.
Training and Safety Data Sheets
Comprehensive training is critical for safe tank operations. Workers need instruction on equipment operation, hazard recognition, and emergency procedures.
Training should cover:
- Proper use of PPE
- Safe handling of chemicals
- Confined space entry procedures
- Fire safety and spill response
Safety Data Sheets (SDS) must be readily available for all chemicals. Workers should know how to access and interpret SDS information.
Regular refresher training keeps safety knowledge current. Document all training sessions and maintain records for compliance purposes.
Compliance with OSHA and Industry Standards
OSHA regulations set minimum safety requirements for tank operations. Employers must comply with standards like:
- 29 CFR 1910.106 (Flammable Liquids)
- 29 CFR 1910.146 (Permit-Required Confined Spaces)
- 29 CFR 1910.119 (Process Safety Management)
Industry-specific standards from organizations like API and NFPA provide additional guidance. These may include:
- API 653 (Tank Inspection, Repair, Alteration, and Reconstruction)
- NFPA 30 (Flammable and Combustible Liquids Code)
Regular audits ensure ongoing compliance. Keep detailed records of inspections, maintenance, and incidents.
Emergency Preparedness and Environmental Safeguards
Develop and practice emergency response plans for potential scenarios like:
- Fires
- Spills
- Leaks
- Medical emergencies
Install appropriate fire suppression systems. Ensure easy access to fire extinguishers and emergency shut-off valves.
Implement spill containment measures:
- Secondary containment structures
- Impermeable liners
- Catch basins
Train employees on proper spill response techniques. Stock spill cleanup materials on-site.
Conduct regular environmental assessments. Monitor for leaks or ground contamination. Implement preventive maintenance to minimize environmental risks.
Operations Involving Tank Equipment
Tank equipment operations require strict adherence to safety protocols to prevent accidents and ensure worker protection. Proper procedures for cleaning, maintenance, material handling, and preventative measures are essential for safe and efficient operations.
Tank Cleaning and Maintenance
Tank cleaning is a critical operation that demands careful planning and execution. Before entry, tanks must undergo vapor and gas freeing (degassing) to eliminate hazardous atmospheres. Atmospheric testing of the tank interior is mandatory to verify safe oxygen levels and absence of toxic gases. Tank isolation, including disconnecting all pipelines and electrical connections, is essential to prevent accidental substance introduction or energization.
For cleaning operations, workers must use appropriate personal protective equipment and follow confined space entry procedures. Removing sludge and debris requires specialized equipment and techniques to minimize worker exposure to harmful substances. Hot work, such as welding or cutting, should only be performed after thorough cleaning and with proper permits in place.
Handling and Storage of Flammable Materials
Safe handling of flammable materials in tank operations is paramount. Storage tanks must be properly labeled and equipped with flame arrestors to prevent fire spread. Transfer operations require grounded equipment to prevent static electricity buildup.
Regular inspections of valves, pumps, and piping systems help identify potential leaks or failures. Implementing a robust maintenance schedule ensures all components function correctly. Workers must be trained in emergency response procedures, including the use of fire suppression systems and evacuation protocols.
Inspection and Corrosion Prevention
Regular inspections are crucial for maintaining tank integrity. Visual checks can identify surface corrosion, while ultrasonic testing detects wall thickness reductions. Cathodic protection systems help prevent corrosion in metal tanks by applying a small electrical current.
Proper coating selection and application protect tank surfaces from corrosive substances. Scheduled maintenance should include reapplication of protective coatings as needed. Monitoring systems can track corrosion rates and alert operators to potential issues before they become critical.
Secondary Containment and Overfill Protection
Secondary containment systems are essential for preventing environmental contamination in case of primary tank failure. These can include concrete berms, double-walled tanks, or impermeable liners. Regular inspection and maintenance of containment areas ensure their effectiveness.
Overfill protection devices, such as high-level alarms and automatic shutoff valves, prevent tank overflows during filling operations. Proper calibration and testing of these systems are crucial for reliable performance. Clear procedures for tank gauging and inventory management help operators prevent overfilling incidents.
Employee training on proper use of overfill protection equipment and response procedures is vital. Regular drills reinforce proper actions during potential overflow scenarios.
Conclusion
Following proper safety standards when using tank equipment is crucial for protecting workers and preventing accidents. Key measures include confined space procedures, atmospheric testing, and appropriate personal protective equipment. Regular training, clear communication protocols, and comprehensive emergency response plans are also essential components of a safe tank operation system. Adhering to established regulations and industry best practices helps ensure the wellbeing of personnel and maintains operational integrity.